Logical Scribbles
[OpenCV] K-means 알고리즘을 사용하여 이미지 군집화 해보기 본문
이번 시간에는 OpenCV를 이용하여 K-means 알고리즘을 통한 이미지 군집화를 구현해보자. K-means 알고리즘에 대해 잘 모른다면 아래 글을 읽고 따라오면 되겠다.
https://stydy-sturdy.tistory.com/19
[기계학습] K-means Clustering 에 대하여
이번 포스팅에서는 기계학습 이론에서 자주 나오는 K-means Clustering에 대해 알아보자. 기계학습은 지도학습과 비지도 학습, 크게 두가지로 나뉜다. 지도 학습은 선생님이 문제를 내고 그 다음 바
stydy-sturdy.tistory.com
이미지 분할(Segmentation)은 비전 분야에서 이미지를 인식하고 분리하는 것에 있어 기초가 된다. OpenCV에서는 이미지 분할을 위한 K-means clustering 알고리즘을 제공하고 있다.
우선 필요한 모듈을 가져오자.
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('K-meansClustering')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import numpy as np
이제 이미지를 출력해보자. 나는 예제를 참고하여 (https://gmnam.tistory.com/168), 분할하기 쉬워보이는 이미지로 먼저 실험을 해 보았다. 이후 복잡한 이미지로도 실험을 진행할 것이다.
image = plt.imread('/content/K-meansClustering/MyDrive/island.jpg')
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
print(image.shape)
출력 결과 이미지의 shape은 3*959*1280임을 확인할 수 있다. 3은 RGB 색상이기 때문에 붙는 수이고, plotting 된 이미지를 보면 가로 1280픽셀, 세로 959 필셀로 이루어져 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
이제 이 이미지를 쫙 펴주자.
vectorized = image.reshape((-1,3))
print(vectorized.shape) # output = (1227520, 3) , 1227520은 959*1280이다.
vectorized = np.float32(vectorized)
print((vectorized))
# Output
# [[182. 165. 175.]
# [188. 172. 182.]
# [239. 228. 234.]
# ...
# [ 2. 181. 211.]
# [ 5. 184. 214.]
# [ 6. 185. 215.]]
RGB 색상을 갖는 한개의 픽셀 단위로 쫙 펴짐을 확인할 수 있다. vectorized된 이미지는 당연하게도 959*1280 = 1227520 의 원소를 갖는다.
이제 본격적으로 k-means알고리즘을 구현해보자.
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 1000, 0.01)
OpenCV를 이용하여 K-means clustering을 하려면, criteria가 필요하다. criteria에는 쉽게 말하면 알고리즘을 중단하는 조건이다.

OpenCV document에서 찾은 글이다. criteria로 설정할 수 있는 것은 총 세가지인데, epsilon값과 max iteration 값을 지정할 수 있다. 나는 epsilon 0.01, max iteration 1000으로 설정하였다.
K = 3
attempts = 10
ret,label,center = cv2.kmeans(vectorized,K,
None,
criteria,
attempts,
cv2.KMEANS_PP_CENTERS)
위 코드에서 K는 군집을 몇 개로 설정할 것인지, attempts는 알고리즘을 몇 번 실행할 것인지(attemps번만큼 실행된 뒤 최적의 결과를 리턴한다.)를 의미한다.
Output 변수로는 ret, label, center를 지정하였다.
- ret (compactness) : 각 데이터 당 자신의 군집의 중심까지의 거리의 제곱의 합이다.
- label : 각 점이 어느 군집에 속해있는지 알려준다.
- center : 군집들의 중심 좌표이다. K개의 좌표가 리턴된다.
또한 위 코드에서 flag를 설정해야 하는데, 초기 중심점이 어디 위치할지 정하는 방법이다. 나는 K-means_PP를 사용하였다.
flags : This flag is used to specify how initial centers are taken. Normally two flags are used for this : cv.KMEANS_PP_CENTERS and cv.KMEANS_RANDOM_CENTERS.
Output 변수들을 출력 해보았다.
print('ret : ', ret)
print('length of label : ',len(label))
print('location of center : ', center)
print('length of center : ', len(center))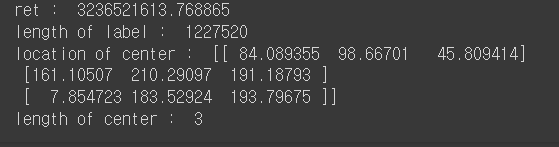
compactness와 label을 갖는 데이터의 길이, 중심의 좌표와 개수를 줄력해 보았다. 당연하게도 label을 갖는 데이터는 1227520개 이고, 중심 좌표의 개수는 설정한 K와 같은 3이 나왔다.
이후 다음의 코드로 군집화가 잘 되었나 확인해 보았다.
A = vectorized[label.ravel()==0]
B = vectorized[label.ravel()==1]
C = vectorized[label.ravel()==2]
plt.scatter(A[:,0],A[:,1])
plt.scatter(B[:,0],B[:,1],c = 'r')
plt.scatter(C[:,0],C[:,1],c = 'g')
plt.scatter(center[:,0],center[:,1],s = 80,c = 'y', marker = 's')
plt.show()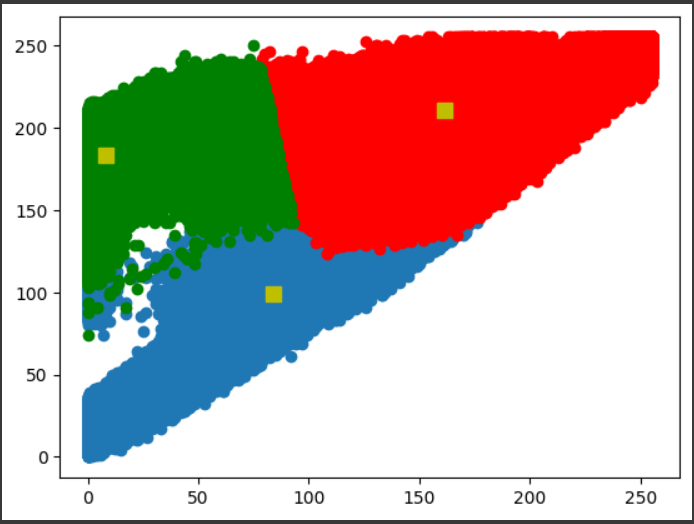
이제 본격적으로 이미지 분할을 해보자.
※ 입력되는 데이터 타입은 반드시 float32여야 한다.
# 이 부분이 중요하다! unit8로 convert back 하고 original이미지 형태로 만들어야 한다
center = np.uint8(center)
res = center[label.flatten()]
result_image = res.reshape((image.shape))
figure_size = 15
plt.figure(figsize=(figure_size,figure_size))
plt.subplot(1,2,1),plt.imshow(image)
plt.title('Original Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(1,2,2),plt.imshow(result_image)
plt.title('Segmented Image when K = %i' % K), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()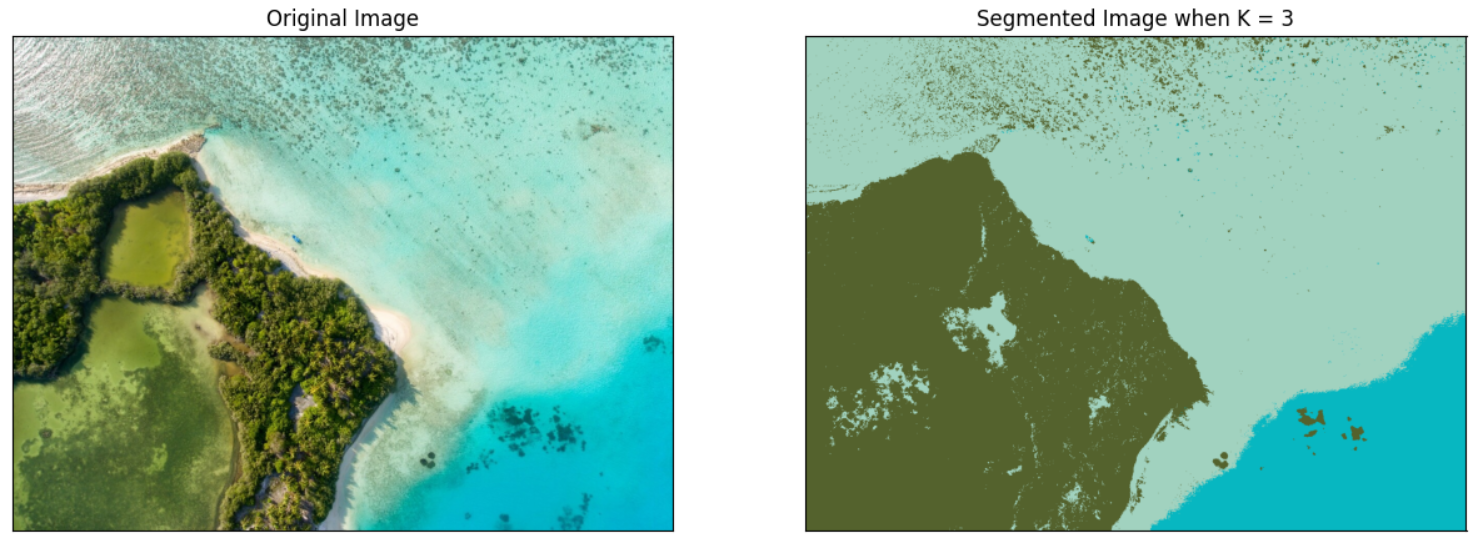
이미지가 3개의 군집으로 잘 분할 되었음을 볼 수 있다.
이제 이 과정을 단일 함수로 표현해보자!
def Kmeanclustering(path,max_iter=1000,eps=0.01,k=3,attempts=10) :
image = plt.imread(path)
vectorized = image.reshape((-1,3))
vectorized = np.float32(vectorized)
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER,max_iter, eps)
ret,label,center = cv2.kmeans(vectorized,k,
None,
criteria,
attempts,
cv2.KMEANS_PP_CENTERS)
center = np.uint8(center)
res = center[label.flatten()]
result_image = res.reshape((image.shape))
figure_size = 15
plt.figure(figsize=(figure_size,figure_size))
plt.subplot(1,2,1),plt.imshow(image)
plt.title('Original Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(1,2,2),plt.imshow(result_image)
plt.title('Segmented Image when K = %i' % k), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
이 함수에 조금 더 복잡해 보이는 사진을 입력해 보았다.

이번에는 K값에 따라 이미지 분할이 어떻게 이루어지나 확인해보자. K=3, 7, 15로 설정하여 확인했다.
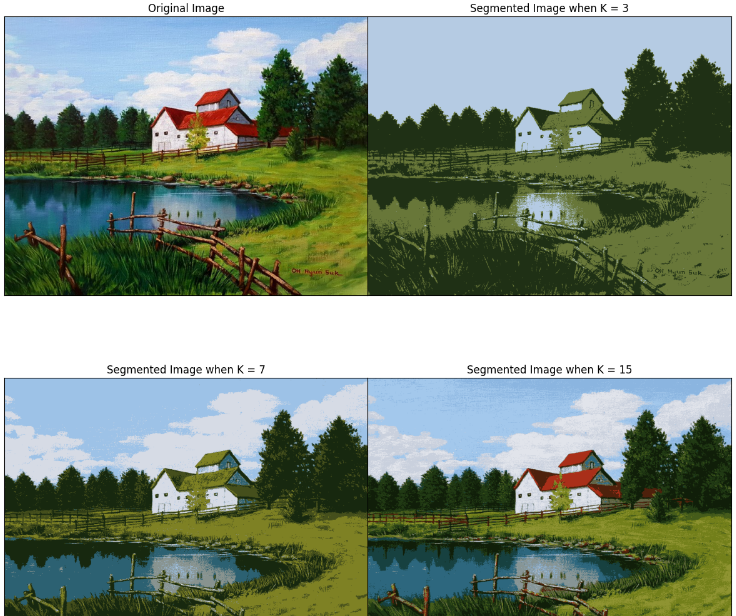
신기하다. 끝!
'딥러닝 > OpenCV' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [OpenCV] 서로 다른 이미지 간 유사도 측정해보기 (0) | 2023.12.06 |
|---|---|
| [OpenCV] 이미지에 Selective Search 적용하고 IoU 계산해보기 (0) | 2023.11.21 |
| [OpenCV] HOG를 이용한 간단한 객체 인식 (0) | 2023.11.14 |



